We Provide Cooling Tower Solution
English
Please Choose Your Language
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-12-29 Origin: Site








Cooling towers are among the most recognizable structures in the power generation industry. From towering hyperbolic shapes rising above thermal power stations to compact mechanical draft units beside industrial plants, cooling towers play a critical role in keeping power plants efficient, stable, and safe. But what exactly is their function, and why are they so indispensable?
Let’s break it down in a clear, practical, and easy-to-understand way.

At its core, a power plant is a massive heat engine. Fuel is burned—or nuclear reactions occur—to produce heat, which is then converted into electricity. However, not all heat can be turned into power. A large portion becomes waste heat, and that heat must go somewhere.
That’s where the cooling tower comes in. Think of it as the lungs of the power plant, continuously releasing excess heat so the entire system can breathe and keep running smoothly.
Most power plants operate on the Rankine cycle. Water is heated into steam, steam spins a turbine, and electricity is generated. Afterward, the steam must be condensed back into water so the cycle can repeat.
Without effective cooling, this loop breaks.
If waste heat isn’t removed efficiently:
Turbine back pressure increases
Power output drops
Fuel consumption rises
Equipment experiences thermal stress
Plant shutdowns become more frequent
In short, poor cooling equals poor performance.
A cooling tower is a heat rejection device. It cools hot circulating water—usually from a condenser—by transferring heat to the atmosphere. This is achieved primarily through evaporative cooling, where a small portion of water evaporates, carrying heat away with it.
Just like sweat evaporating from your skin cools your body, water evaporating inside a cooling tower lowers the temperature of the remaining water. Simple physics, powerful results.
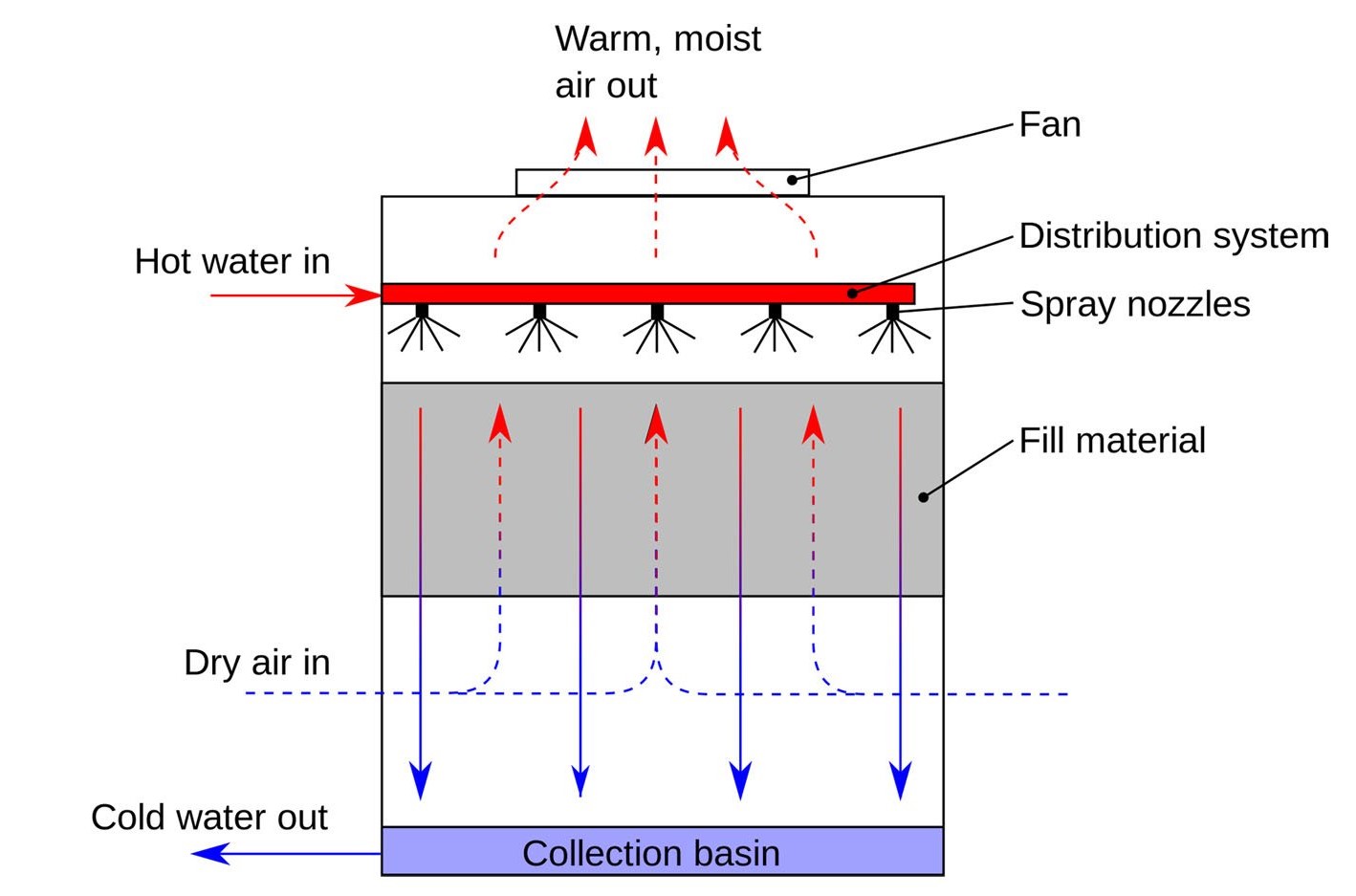
The main function of a cooling tower in a power plant is to cool down condenser water after it absorbs heat from exhaust steam. This cooled water is then reused in the condenser, forming a continuous and efficient loop.
Lower condenser temperatures mean lower turbine back pressure. That directly translates into higher efficiency, better fuel economy, and increased power output.
These are the iconic hyperbolic cooling towers seen at large thermal and nuclear power plants. They rely on natural air movement created by temperature and density differences—no fans required.
They are ideal for:
Very large heat loads
Long-term continuous operation
Lower operating energy costs
Mechanical draft towers use fans to move air and are more compact and flexible.
Induced draft towers pull air from the top, offering better efficiency and uniform airflow
Forced draft towers push air from the bottom and are easier to access for maintenance
Wet cooling towers are the most common in power plants because they offer:
Higher cooling efficiency
Lower capital costs
Proven, reliable performance
In regions with limited water resources, dry cooling towers reduce water consumption significantly. While they require higher investment and have lower thermal efficiency, they help meet strict environmental and water-use regulations.
In coal-fired and gas-fired power plants, cooling towers complete the Rankine cycle. Without them, steam could not be condensed efficiently, making continuous operation impossible. Simply put, no cooling tower, no power generation.
In nuclear power plants, cooling towers play a crucial safety role. They remove heat not only during normal operation but also after shutdown. Effective cooling ensures reactor stability and protects both equipment and personnel.
Modern cooling towers are designed to minimize water loss through:
High-efficiency drift eliminators
Optimized water distribution systems
Advanced fill materials
By dissipating heat into the atmosphere instead of discharging hot water into rivers or lakes, cooling towers help prevent thermal pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems.
Cooling tower performance depends heavily on local climate. Cooler, drier air improves evaporation and heat rejection.
High-quality fill increases the contact area between air and water, improving heat transfer and overall efficiency.
Today’s cooling towers integrate:
Variable-speed fans
Intelligent control systems
Corrosion-resistant materials
These advancements reduce operating costs while maximizing thermal performance.
As a professional cooling tower manufacturer, Mach Cooling
https://www.machcooling.com/
provides high-efficiency cooling towers, customized engineering solutions, and reliable after-sales support for power plants worldwide. Their products are designed to balance performance, durability, and sustainability, helping power plants operate at peak efficiency.
Cooling towers do not emit smoke—what you see is water vapor
They do not waste excessive water when properly designed
Modern cooling towers are safe, efficient, and environmentally compliant
The future of cooling towers includes:
Hybrid wet–dry systems
AI-driven performance optimization
Ultra-low water consumption designs
Sustainability and efficiency will continue to shape cooling tower innovation.

The function of a cooling tower in a power plant is far more than just cooling water. It ensures efficient power generation, operational safety, environmental protection, and long-term reliability. Whether in thermal or nuclear power plants, cooling towers are an essential backbone of modern energy systems.
By choosing a trusted manufacturer like Mach Cooling, power plant operators can achieve higher efficiency today while preparing for a more sustainable future tomorrow.