We Provide Cooling Tower Solution
English
Please Choose Your Language
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-13 Origin: Site








Every industrial system that generates power, cools buildings, or runs heavy processes has one invisible enemy—excess heat. If that heat isn’t removed efficiently, performance drops, energy costs rise, and equipment life shortens dramatically. That’s where cooling towers step in.
In this article, we’ll clearly explain the purpose of a cooling tower in heat rejection systems, how it works, why it’s essential across industries, and how professional cooling tower solutions—such as those supported by Mach Cooling—help industries manage heat safely and efficiently.
Heat rejection is rarely the star of an industrial operation, yet it’s the reason everything else can function. Whether it’s a turbine spinning in a power plant or a chiller cooling a skyscraper, heat must be removed continuously.
Think of heat rejection like breathing. You don’t think about it—until it stops.
A cooling tower is a heat rejection device that removes unwanted heat from warm circulating water and transfers it to the atmosphere, mainly through evaporative cooling. Once cooled, the water is reused, creating an efficient and sustainable cooling cycle.
Every system has a temperature limit. Exceed it, and efficiency collapses.
Without proper heat rejection:
Equipment overheats
Production efficiency declines
Maintenance costs surge
Unplanned shutdowns occur
Running an industrial plant without effective heat rejection is like driving uphill with the parking brake on—it works, but not for long.
Most cooling systems operate in closed loops. Heat enters through processes and must exit somewhere. Cooling towers provide that essential exit path.
The primary purpose of a cooling tower is to reject excess heat from industrial systems. By lowering water temperature, cooling towers allow equipment to operate within safe limits.
Stable temperatures mean predictable performance, longer equipment life, and lower energy consumption. Cooling towers act as thermal stabilizers for entire facilities.
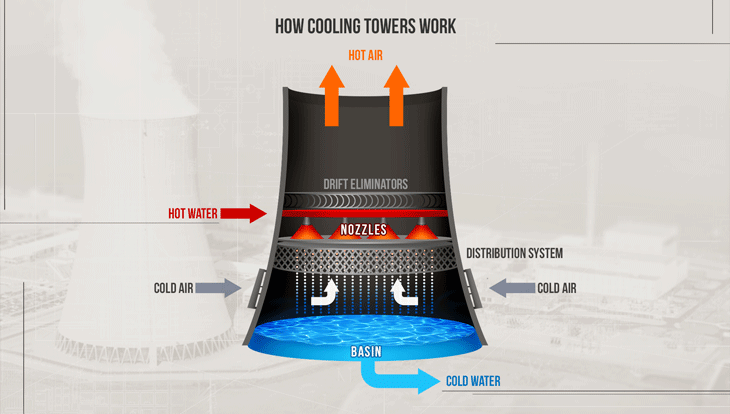
Hot water enters the cooling tower and is distributed over fill material. As air flows through the tower, a small portion of the water evaporates—carrying heat away with it.
Evaporation is incredibly efficient. When water changes from liquid to vapor, it absorbs large amounts of heat, cooling the remaining water.
Airflow—either natural or fan-driven—accelerates evaporation and enhances heat transfer.
Only a small percentage of water evaporates, but that small loss does most of the cooling work.
In power plants, cooling towers reject waste heat from condensers, enabling turbines to operate efficiently and safely. Without cooling towers, continuous power generation would be impossible.
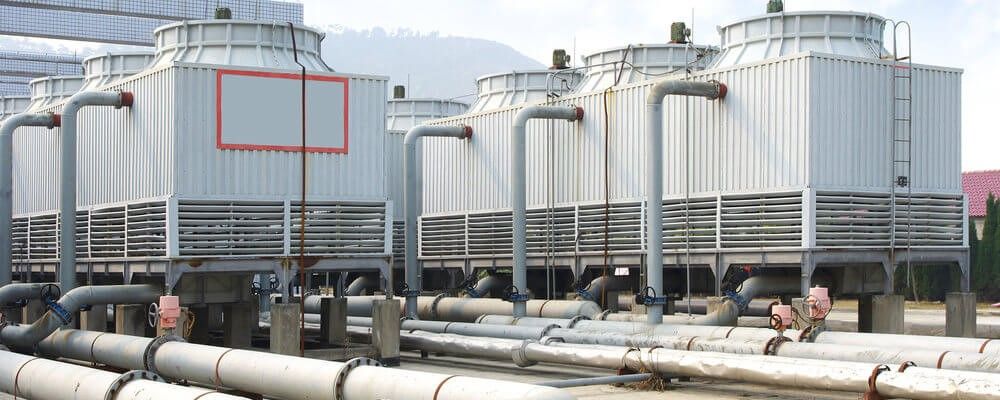
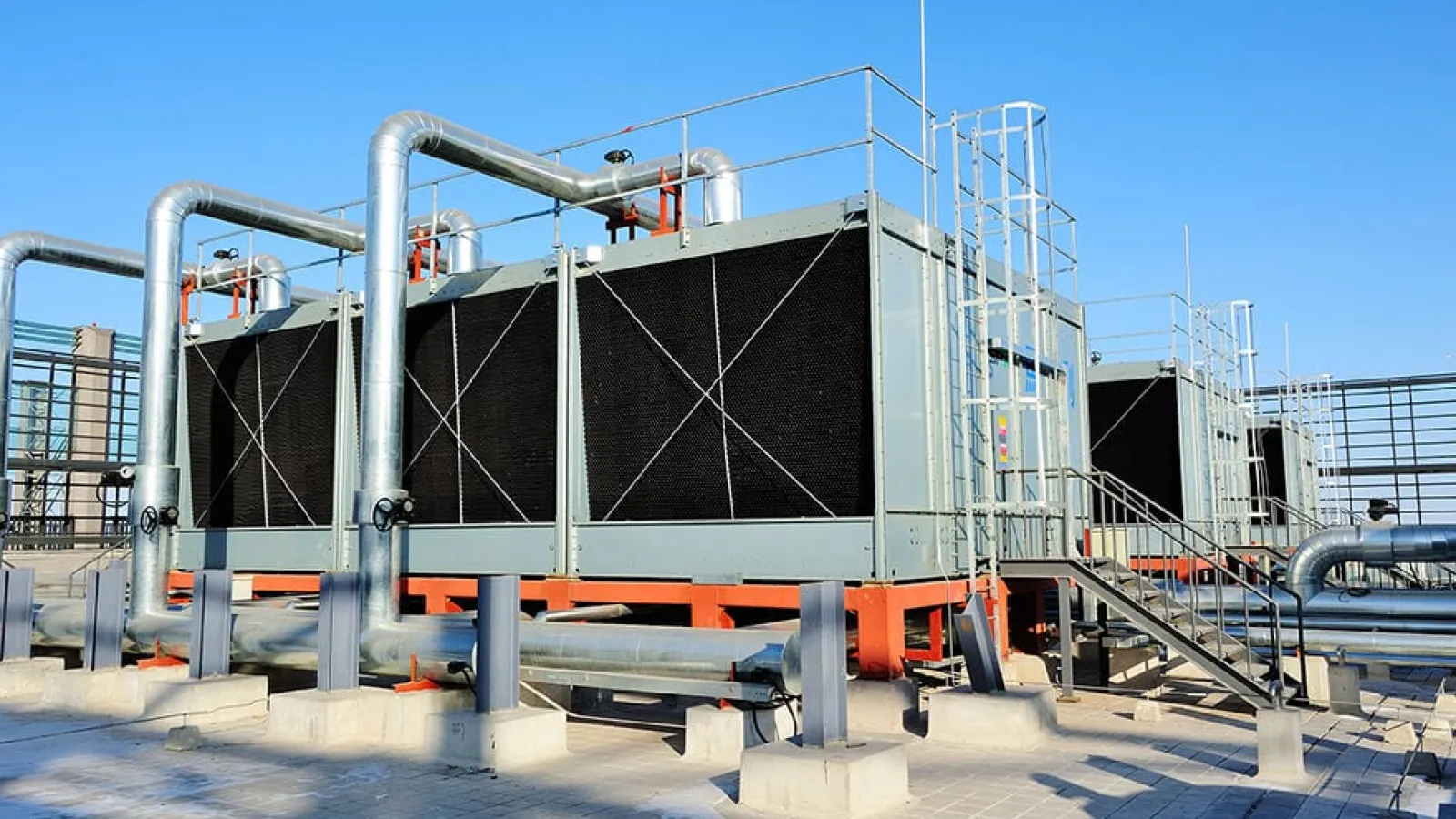


Large commercial buildings rely on cooling towers to support chillers. They remove heat collected from indoor spaces, keeping occupants comfortable while controlling energy use.

Steel mills, chemical plants, refineries, and food processing facilities depend on cooling towers to protect equipment and maintain product quality.
These massive hyperbolic towers rely on buoyancy-driven airflow and are commonly used in large power generation projects.
Fan-assisted towers offer controlled airflow, compact footprints, and high efficiency—ideal for industrial and HVAC applications.
Fill material increases surface area, maximizing contact between air and water and significantly improving heat rejection.
Drift eliminators capture water droplets, reducing water loss and protecting surrounding equipment and environments.
Fans regulate airflow, ensuring consistent cooling performance under varying load conditions.

By lowering system temperatures, cooling towers reduce energy consumption and improve overall plant efficiency—often delivering significant operational savings.
Modern cooling towers are designed to:
Minimize water loss
Optimize blowdown rates
Reduce thermal discharge into natural water bodies
These features help industries meet environmental and regulatory requirements.
An undersized or poorly designed cooling tower can compromise the entire heat rejection system. Proper thermal design, airflow management, and material selection are essential for long-term reliability.
Cooling towers are not one-size-fits-all products. Experienced manufacturers provide:
Customized thermal design
Durable materials
Performance optimization
Long-term service reliability

Mach Cooling (https://www.machcooling.com/) delivers engineered cooling tower solutions for industrial, power generation, and HVAC applications. With a focus on thermal efficiency, structural durability, and reliable performance, Mach Cooling supports heat rejection systems that operate efficiently under demanding conditions.
The purpose of a cooling tower in heat rejection systems goes far beyond cooling water. Cooling towers protect equipment, stabilize processes, reduce energy consumption, and support sustainable industrial operations.
From power plants to factories and commercial buildings, cooling towers quietly perform one of the most important jobs in modern industry—removing heat so everything else can function. And with well-designed systems supported by experienced manufacturers like Mach Cooling, industries can rely on efficient, long-term heat rejection solutions.