We Provide Cooling Tower Solution
English
Please Choose Your Language
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-22 Origin: Site








Water is no longer a low-cost utility that operators can afford to ignore. Across industrial plants, HVAC systems, and power stations, rising water prices and tighter environmental regulations are forcing facility managers to rethink how cooling systems are operated.
One of the most powerful—but often misunderstood—levers for reducing cooling tower water consumption is optimizing cycles of concentration. When managed correctly, cycles of concentration can dramatically reduce makeup water demand, wastewater discharge, and overall operating costs without compromising system reliability.
In simple terms, better cycle control means doing more with the same water.

Cooling tower cycles of concentration (COC) describe how many times dissolved minerals are concentrated in the circulating water compared to the incoming makeup water.
Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
Cycles of Concentration = Concentration in Circulating Water ÷ Concentration in Makeup Water
If a cooling tower operates at five cycles, the dissolved solids in the system water are five times higher than in the makeup supply.
Each additional cycle represents water being reused instead of discharged. Higher cycles mean:
Less blowdown
Lower makeup water demand
Reduced sewer and treatment costs
However, cycles must always be balanced against system limitations such as scaling, corrosion, and fouling.
Cooling towers reject heat primarily through evaporation. When water evaporates, pure water vapor leaves the system while minerals remain behind. Over time, these minerals accumulate.
To prevent excessive buildup, a portion of concentrated water is discharged as blowdown, and fresh makeup water is added. The ratio between evaporation and blowdown defines the achievable cycles of concentration.
Operating at low cycles leads to excessive blowdown, which results in:
Higher water consumption
Increased wastewater volumes
Elevated chemical usage
Many systems still run at two or three cycles simply because they always have—leaving significant water savings untapped.
Typical operating ranges vary by application:
HVAC cooling towers: 4–6 cycles
Industrial process cooling: 6–10 cycles
High-efficiency systems: 10+ cycles
Pushing cycles too high without proper controls can lead to scale formation, corrosion, and biological growth. Optimization is not about maximizing cycles blindly—it’s about achieving the highest safe and sustainable cycles.
The most common calculation uses conductivity:
Cycles = Tower Conductivity ÷ Makeup Conductivity
This method is widely adopted because it is simple, reliable, and easy to automate.
Chloride concentration provides a stable alternative when conductivity fluctuates. Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) analysis is also used for periodic verification.
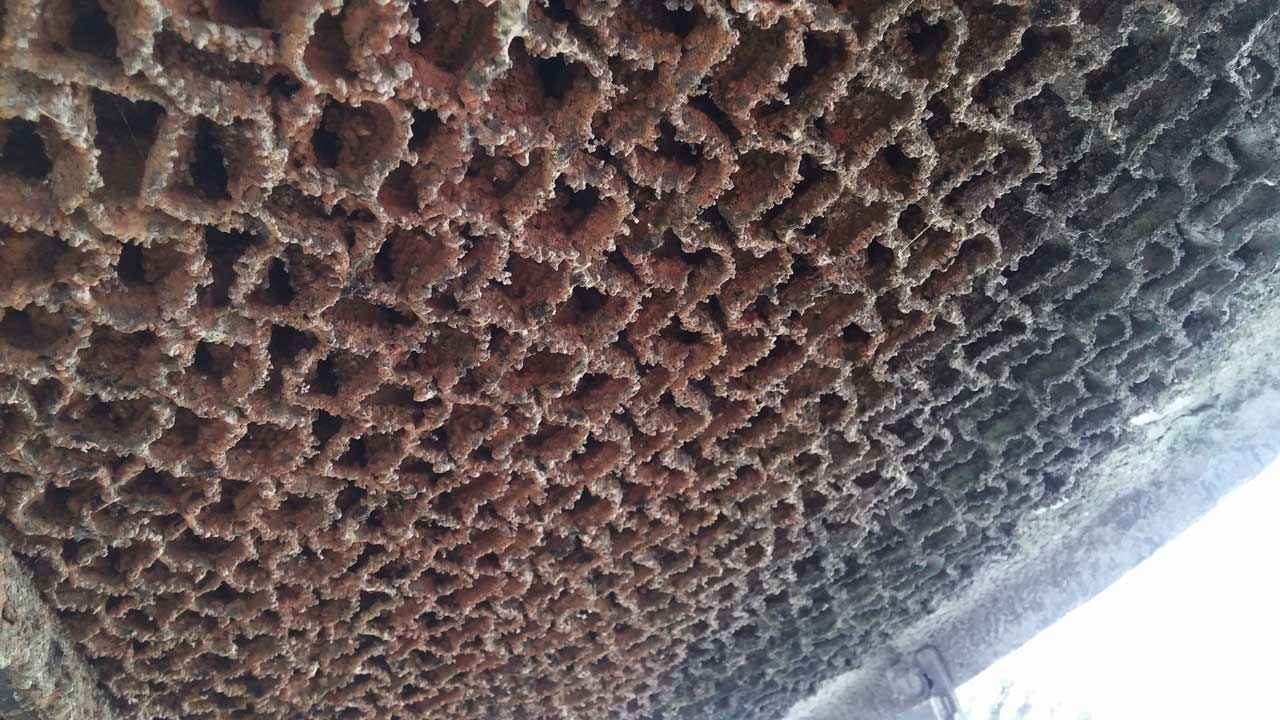



As mineral concentration increases, calcium carbonate and other salts may precipitate. Scale acts as an insulating layer on heat transfer surfaces, reducing efficiency and increasing energy costs.
Unbalanced chemistry at either very high or very low cycles can accelerate corrosion and encourage biological fouling, threatening both performance and equipment life.
The safest approach is gradual adjustment combined with continuous monitoring. Raising cycles should always be supported by proper water treatment and filtration.
Modern scale inhibitors and dispersants allow systems to operate at higher cycles without deposition. A professional treatment program is essential for stable operation.
Side stream filtration removes suspended solids that act as nucleation points for scale, making higher cycles more achievable.

Manual blowdown is imprecise and often leads to excessive water loss. Automated blowdown systems adjust discharge based on real-time conductivity measurements, ensuring consistent cycles.
Conductivity controllers function like thermostats for water quality—maintaining optimal cycles automatically while minimizing operator intervention.
Advanced polymer-based inhibitors prevent crystal growth even at elevated mineral concentrations.
Balanced corrosion inhibitors protect carbon steel, stainless steel, and copper alloys simultaneously, ensuring long-term system integrity.
Increasing cycles from three to six can reduce makeup water usage by up to 40 percent, delivering immediate operational savings.
Lower blowdown volumes reduce wastewater discharge, simplify regulatory compliance, and support corporate sustainability goals.
Commercial buildings benefit from stable cycle control and automated monitoring, especially in water-stressed regions.
For power generation facilities, optimized cycles are critical for balancing efficiency with water availability.
Industries such as chemicals, food processing, and metals rely on high-cycle operation to control costs and improve reliability.
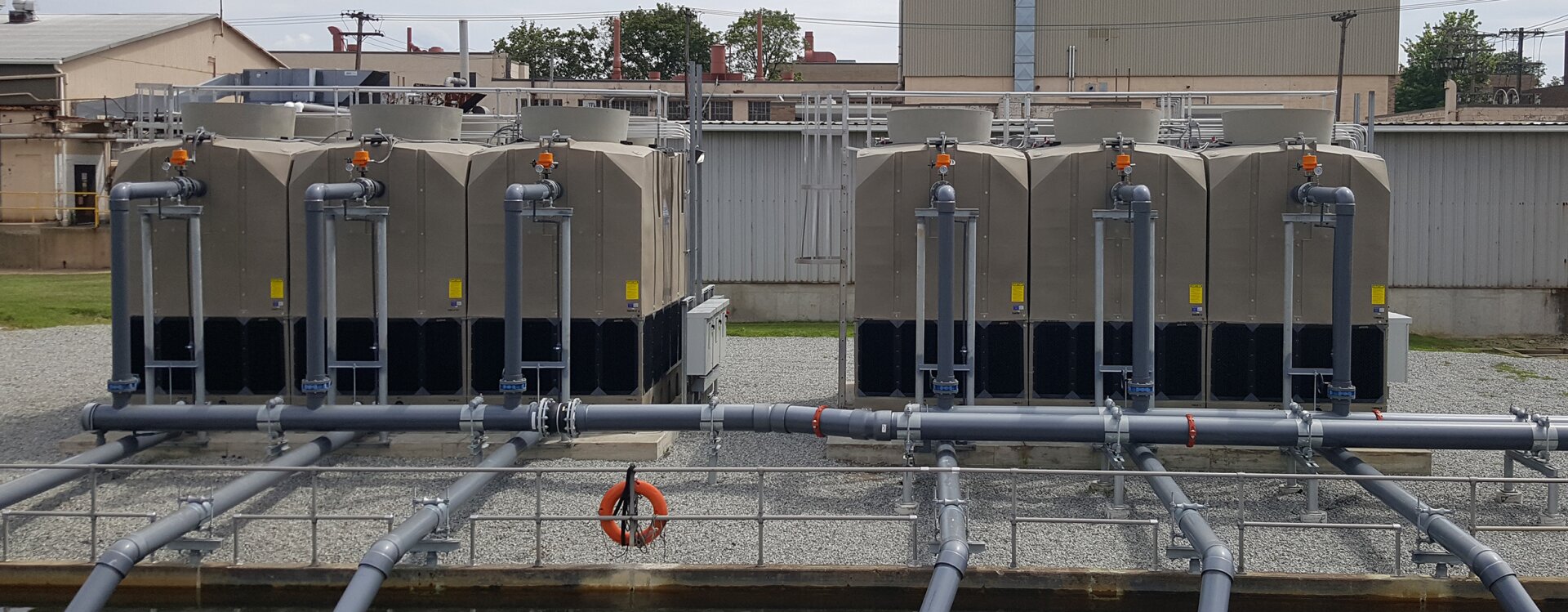

Optimizing cycles of concentration starts with properly designed equipment. Mach Cooling (https://www.machcooling.com/) provides cooling towers engineered for high-efficiency water use, durable construction, and stable performance under elevated cycles of concentration.
Their solutions are widely applied in industrial, HVAC, and power plant projects, helping customers achieve long-term water savings while maintaining operational safety.
Monitor conductivity regularly
Automate blowdown control
Implement professional water treatment
Use side stream filtration
Partner with an experienced cooling tower manufacturer

Optimizing cooling tower cycles of concentration is one of the most effective strategies for reducing water consumption and operating costs. When supported by proper controls, water treatment, and high-quality equipment, higher cycles translate directly into savings and sustainability.
With modern technologies and reliable manufacturers like Mach Cooling, achieving efficient, high-cycle cooling tower operation is no longer a challenge—it’s a competitive advantage.