We Provide Cooling Tower Solution
English
Please Choose Your Language
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-29 Origin: Site








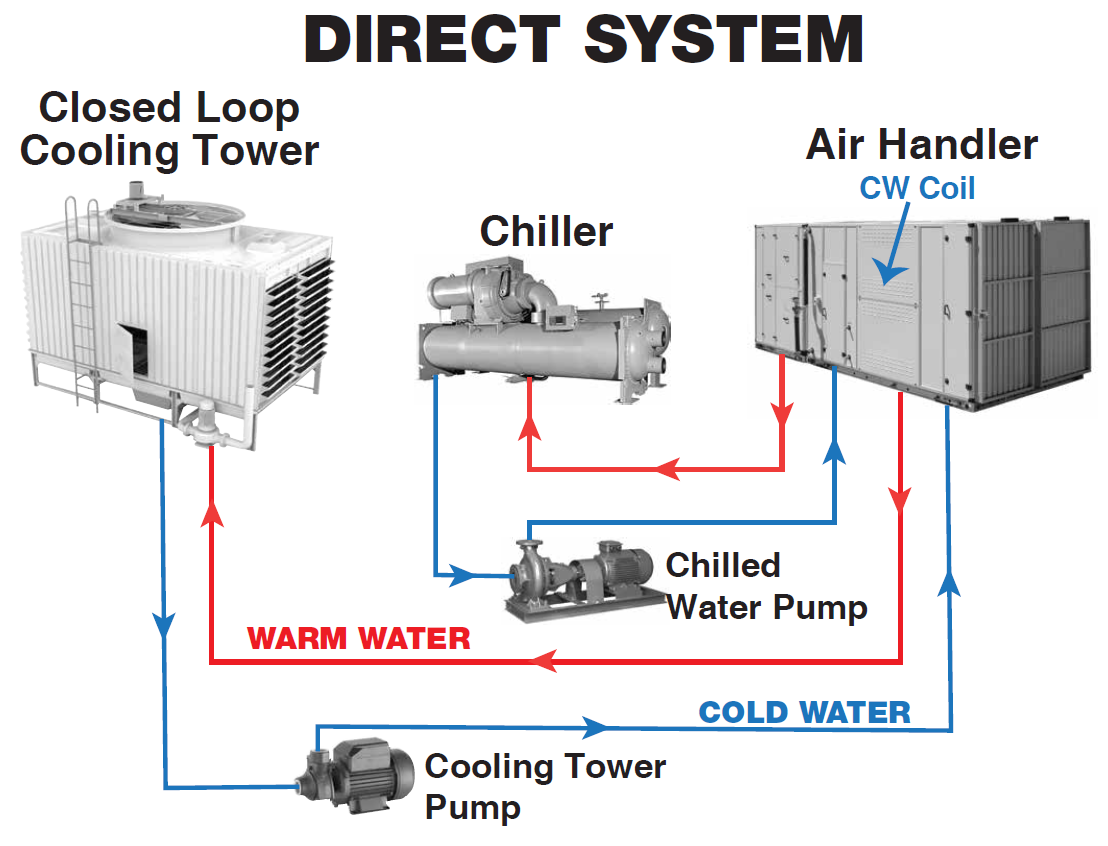
In industrial cooling systems, HVAC, and large water circulation systems, selecting the correct cooling tower tonnage is critical. Tonnage affects:
Cooling tower capacity matching
Circulating water flow
Heat transfer performance
System reliability, energy efficiency, and operational stability
This article explains the definition of cooling tower tonnage, common calculation formulas, required parameters, example calculations, and how to verify and adjust tonnage according to real-world conditions. It also includes images and a table template for easy reference.
In refrigeration and cooling:
1 refrigeration ton (RT) = 12,000 BTU/h. (sciencing.com)
For cooling towers, 1 ton is often defined as 15,000 BTU/h to account for condenser efficiency losses. (engineersdaily.com)
This means a cooling tower rated at N tons can theoretically dissipate N × 15,000 BTU/h of heat.
Cooling tower capacity depends on circulating water flow and the water temperature difference (ΔT). A common formula is:
Cooling Tower Capacity (tons) = (500 × Q × ΔT) / 12,000
Where:
Q = Water flow rate (GPM)
ΔT = Temperature difference between inlet and outlet (°F)
500 = fluid factor accounting for water density, specific heat, and unit conversion (deltacooling.com)
This converts heat removed by the tower into an equivalent “ton” for easier comparison with chiller capacity.
To calculate tonnage accurately, collect:
Circulating water flow Q (GPM)
Hot water inlet temperature T₁ and cold water outlet temperature T₂ → ΔT = T₁ − T₂
Heat load (BTU/h or kW) or chiller tonnage
Environmental/design conditions (wet bulb temperature, efficiency, safety margin)
For Mach Cooling towers, these data usually come from design specs, pumps, piping, and the cooling system.
Given:
Flow Q = 500 GPM
T₁ = 100 °F, T₂ = 85 °F → ΔT = 15 °F
CTC = 500 × 500 × 15 ÷ 12,000 = 3,750,000 ÷ 12,000 ≈ 312.5 tons
So, the tower’s theoretical cooling capacity is approximately 312.5 tons.
If the connected chiller is 250 RT, a 312.5-ton tower provides sufficient capacity for condenser heat dissipation, ensuring stable operation.
1 chiller RT = 12,000 BTU/h
Cooling tower tonnage ≈ 15,000 BTU/h per ton → Cooling tower tonnage = Chiller RT × (12,000 / 15,000) ≈ 0.8 × chiller tons
To account for system losses, the cooling tower tonnage should usually equal or slightly exceed the chiller tonnage (engineersdaily.com)
Calculate total system heat load (BTU/h) or determine chiller tonnage
Use circulating water flow and ΔT to estimate required tower tonnage
Consider environmental conditions, system efficiency, safety margin → adjust tonnage accordingly
Compare with Mach Cooling product specs and recommended flow/ΔT
Verify water system (pumps, piping, flow) ensures design conditions are met


| Item | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Circulating Water Flow Q | ______ GPM |
| Hot Water Inlet T₁ | ______ °F |
| Cold Water Outlet T₂ | ______ °F |
| ΔT = T₁ − T₂ | ______ °F |
| Calculated Cooling Tower Tonnage | = 500 × Q × ΔT ÷ 12,000 = ______ tons |
| Recommended Tonnage (with margin) | ______ tons |
| Chiller Tonnage | ______ tons |
| Cooling Tower Model / Notes (Mach Cooling) | __________________ |
ΔT must be in °F, Q in GPM.
For metric systems, convert m³/h and °C to GPM and °F or use heat-load-based calculations.
Factory-rated tonnage assumes standard conditions.
Temperature difference, wet-bulb temp, airflow, and water distribution affect actual capacity → always leave a safety margin.
Matching tower tonnage to chiller tonnage is not enough.
Consider piping, pumps, ambient conditions, and operational scenarios.
For high ΔT, low/high flow, or frequent start/stop, consult Mach Cooling for confirmation.
Mach Cooling towers are engineered for water/air contact efficiency, durability, and optimized flow distribution. Accurate tonnage calculations allow you to leverage the tower’s full performance.
Ensures effective cooling
Reduces pump/fan energy use
Minimizes water usage and treatment costs
Extends equipment life
Correct tonnage selection provides buffer against load fluctuations, ambient temperature changes, and water quality variations, improving system stability.
Calculating and selecting the proper cooling tower tonnage is essential in design, procurement, and maintenance. This article provides:
Definition and calculation formulas
Required parameters and sample calculations
Notes, tips, and matching guidance for Mach Cooling products
For practical projects:
Collect accurate flow and temperature data
Use formulas and templates for estimation
Consider system efficiency, environment, and safety margin
Verify with Mach Cooling product specs and operational conditions