We Provide Cooling Tower Solution
English
Please Choose Your Language
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-06 Origin: Site








When it comes to keeping large buildings, industrial plants, or data centers cool and comfortable, HVAC systems often rely on unsung heroes — cooling towers. Tucked beneath that massive structure is a component you might easily overlook: the cooling tower basin.
But trust me — this basin is more than just a pool of water. It’s where heat energy gets released, where water gets collected, and where the efficiency of your entire system can be won or lost. If you’re responsible for an HVAC system, facilities management, or you’re just curious about how these massive beasts work, buckle up. We’re going deep (but in a fun way).
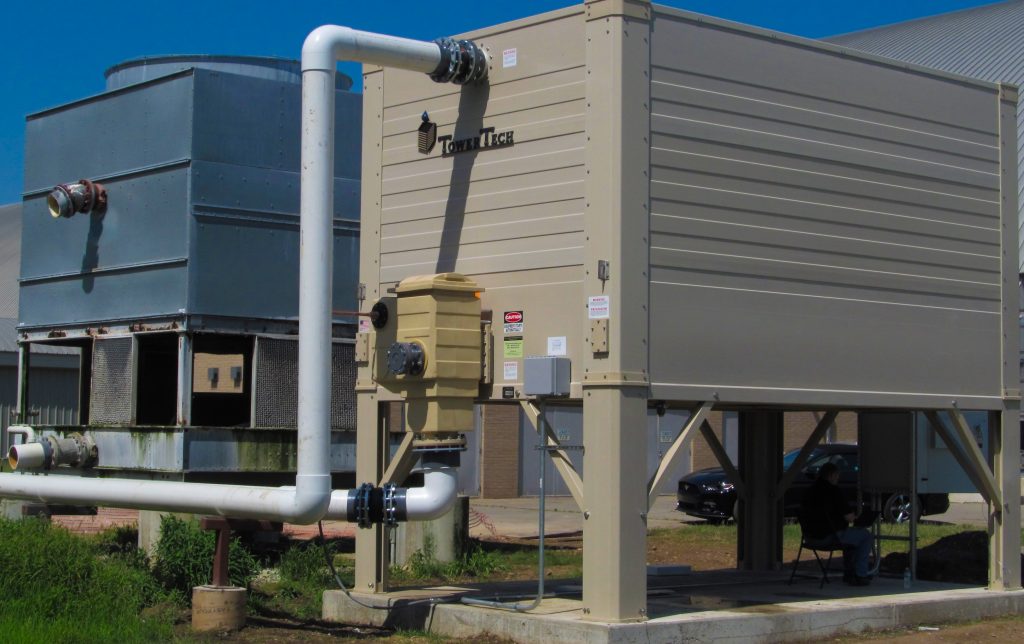

At its simplest, the cooling tower basin is the bottom section of a cooling tower where water collects after it cascades down through the fill media. Think of it as the “catch basin” or reservoir that gathers water that’s been cooled by air and is ready to be pumped back into the system.
If the cooling tower were a water fountain, the basin would be the pool at the base — always ready to receive more water, always keeping things in balance.
To picture it in context, imagine this flow:
Hot return water from your HVAC system enters the cooling tower.
It travels over fill media, exchanging heat with air.
That now‑cooler water falls into the cooling tower basin.
From the basin, pumps send water back into the HVAC loop.
The basin sits at the heart of this cycle, ensuring water is ready and waiting at the right temperature and volume.
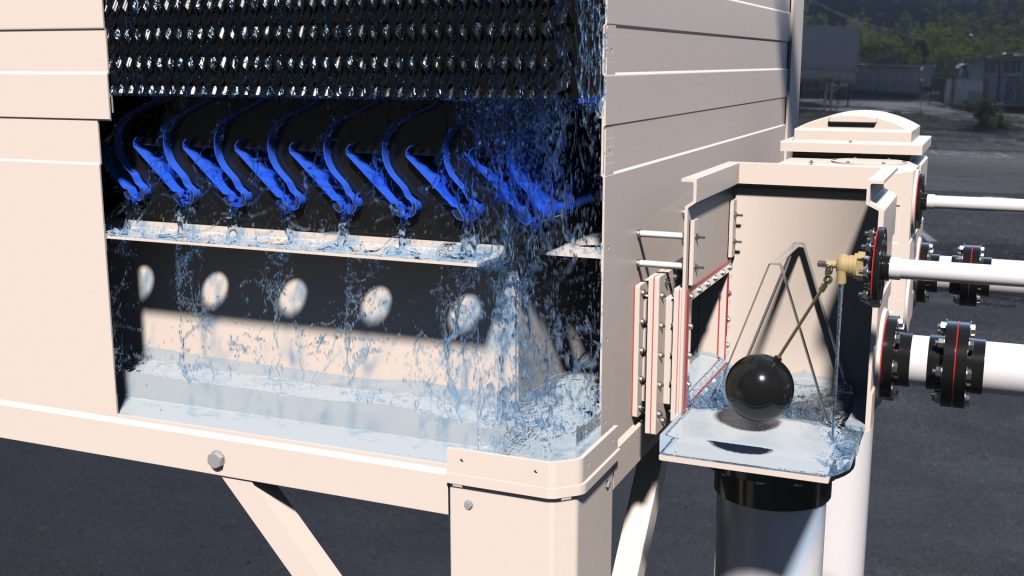
Before we go further, it helps to distinguish two common cooling tower types:
Open Loop Towers – expose water directly to air, and the cooled water is circulated back into the chilled water loop.
Closed Loop Towers – use coils or heat exchangers so the HVAC fluid never directly contacts the makeup or basin water.
Regardless of type, the basin functions as the reservoir where cooled water collects — vital in both systems.
In most HVAC cooling tower setups, the water doesn’t just fall and collect once. It cycles through the basin, gets pumped up, falls over the fill again, and repeats — thousands of times a day. This continuous loop is what keeps your building comfortable even under extreme outdoor temperatures.
A cooling tower basin has to handle water continuously. Common materials include:
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) – corrosion‑resistant and lightweight
Concrete – rock solid and durable
Stainless Steel – high resistance to corrosion but costlier
PVC or Polymer Linings – protective coatings that prolong life
Each material has trade-offs: concrete is sturdy but heavy, FRP is corrosion-resistant but harder to repair. The choice depends on your environment and budget.
A good basin has:
Sloped bottoms to guide water toward the pump suction area
Reinforced edges to handle stress
Drains or sumps for maintenance and cleaning
Overflow points to prevent flooding
These features reduce maintenance problems and ensure smooth operation.
Basins come in many sizes — from small rooftop cooling towers on office buildings to industrial giants serving factories or data centers. Basins are sized to match the heat load and pumping capacity of the HVAC system.
The basin is where the final stage of heat rejection is completed. Water that’s been exposed to air across the fill enters the basin cooler. From here, it’s stored briefly until pumps pull it back through the system.
It also acts as a buffer — if demand spikes or pumps slow, the basin provides a cushion of ready-to-use water.
A properly designed basin prevents water from splashing all over the place. Too much splashback means:
Water loss
Increased maintenance
Corrosion around the tower
A good basin collects water quietly and efficiently.
Water treatment prevents scale, bacteria, and corrosion. The basin supports continuous water treatment to keep it clean, balanced, and safe for recirculation.
Even the simplest components have challenges.
Hard water carries minerals that settle at the bottom over time. If left unchecked, sediment:
Reduces basin capacity
Interferes with pumps
Reduces heat-transfer efficiency
Regular cleaning is essential.
Even corrosion‑resistant materials can degrade over years of wet/dry cycles. Material choice and protective coatings matter.
Stagnant water is a breeding ground for bacteria — including Legionella. Basin cleanliness and water treatment are critical to safety.
At least quarterly (or more in harsh environments):
Empty and clean the basin
Scrub away mineral deposits
Check lining conditions
Clean basins equal better system performance.
Work with water treatment specialists to balance:
pH levels
Corrosion inhibitors
Scale preventers
Biocides
This prevents damage and ensures efficiency.
Check basin walls, drains, pumps, and water clarity. Keep a log — early trends help you catch issues before they escalate.
Manufacturers like Mach Cooling (https://www.machcooling.com/) provide high-performance cooling tower solutions for all HVAC systems.
Advantages include:
Durable basin designs
Corrosion-resistant materials
Custom solutions to match heat load requirements
Support for maintenance and service
Choosing a basin from a trusted brand reduces surprises and improves uptime.
Every building has unique cooling needs. Mach Cooling offers tailored basin options so your tower performs at peak efficiency — whether it’s for a data center, hospital, or office building.
Expect basins to become smarter and greener:
Advanced composites – lighter, longer life
Sensor integration – real-time monitoring
AI-assisted maintenance predictions
Eco-friendly water treatment
These innovations promise easier management and improved reliability.
The cooling tower basin may look like a simple pool of water, but it’s critical in any HVAC cooling tower system. It stores cooled water, supports heat rejection, buffers demand changes, and plays a key role in water treatment.
Keeping it clean, well-designed, and properly matched to your HVAC load ensures energy efficiency and long equipment life. With expert partners like Mach Cooling, your basin and your entire cooling system are ready to perform day in and day out.

Cooling Tower System Layout: From Water Inlet To Heat Rejection
Online Cooling Tower Resources for Engineers And Contractors
The Role of Cooling Tower Filtration in Water Quality Management
Understanding The Role of A Cooling Tower Basin in HVAC Systems
Advantages of Cross Flow Cooling Towers in Industrial Applications
Optimizing Cooling Tower Blowdown for Water And Energy Efficiency