We Provide Cooling Tower Solution
English
Please Choose Your Language
Views: 0 Author: Lisa Publish Time: 2025-09-30 Origin: Site








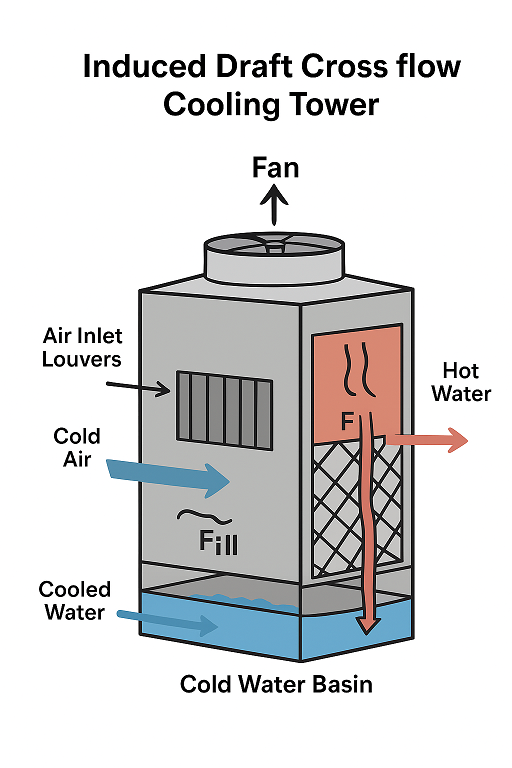
An induced draft cross flow cooling tower is a mechanical draft cooling tower where air is drawn horizontally across the falling water stream by a fan located at the top of the tower. It’s one of the most common designs used in HVAC systems, power plants, and industrial processes.
1. Hot water from the process enters the tower at the top and is distributed over the fill (heat exchange media).
2. Air is drawn horizontally across the tower by fans mounted at the top (induced draft).
3. The airflow crosses the falling water stream (cross flow) — cooling occurs via evaporation and heat transfer.
4. Cooled water collects in the basin at the bottom and returns to the system.
5. Warm, moist air is discharged at the top of the tower.
| Component | Function |
| Fan (Induced Draft) | Pulls air through the fill and discharges it upward |
| Fill (Heat Exchange Media) | Increases water surface area for better heat transfer |
| Water Distribution System | Sprays or distributes hot water over the fill |
| Air Inlet Louvers | Allow air to enter horizontally and prevent splash-out |
| Drift Eliminators | Minimize water droplets leaving with exhaust air |
| Cold Water Basin | Collects cooled water for recirculation |
| Casing/Structure | Supports all internal components |
Cross flow design: Air moves horizontally, water falls vertically.
Induced draft: Fan at the top pulls air, providing stable airflow.
Easy maintenance: Components like distribution basins are accessible.
Good performance: Efficient for a wide range of applications.
Less pumping head: Water flows by gravity into the fill.
✅ Stable airflow due to induced draft
✅ Quieter than forced draft types
✅ Easier access for maintenance
✅ Lower fan power requirement
HVAC systems in commercial buildings
Industrial cooling (chemical, food processing)
Power generation plants
Cooling Tower for Sale – High Efficiency, Factory Direct Supply
Cooling Tower Capacity Vs Load: Matching Performance To Demand
Best Cooling Tower for Energy Efficiency And Low Operating Cost
Approach Temperature Vs Range in Cooling Towers: Key Differences
American Chillers And Cooling Tower Systems: Quality, Performance, And Reliability