We Provide Cooling Tower Solution
English
Please Choose Your Language
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-12-15 Origin: Site








In any industrial or HVAC application, the performance of a water cooling tower depends not only on water circulation but also on how effectively air flows through the system. Air flow rate determines how much heat can be removed from hot circulating water and directly impacts energy efficiency, cooling stability, and cooling tower water use.
This article explains how to calculate air flow rate in a cooling tower, covering theory, formulas, and practical engineering considerations. It applies to various configurations, including water cooled tower, water cooling tower system, and closed loop cooling tower designs. The discussion also aligns with proven engineering practices adopted by professional manufacturers such as Mach Cooling (https://www.machcooling.com/).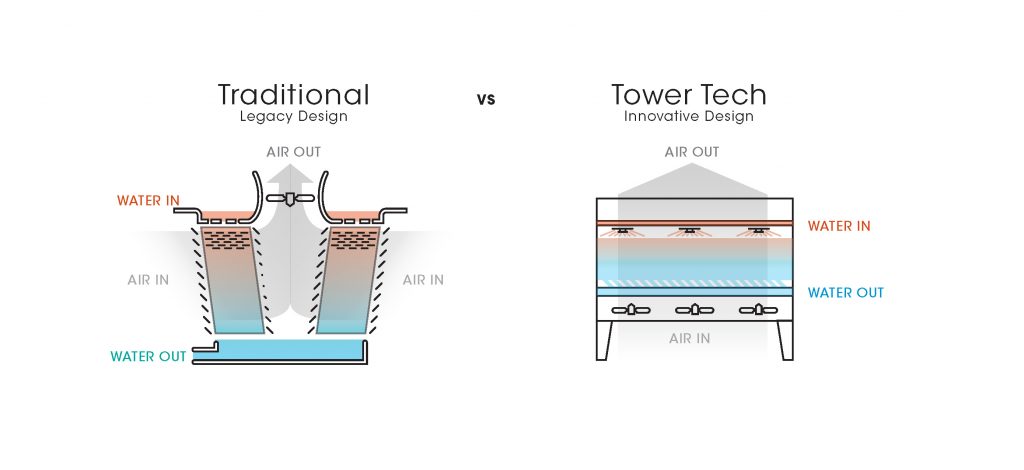
A cooling tower removes heat by bringing warm water into contact with ambient air. As air passes through the tower:
Sensible heat is transferred from water to air
A small portion of water evaporates, removing latent heat
This process makes air flow the primary driver of cooling performance in any water cooling tower system.
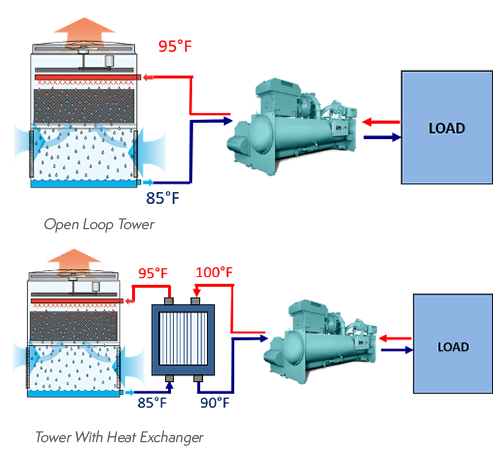
Different cooling tower designs influence how air flow is calculated:
Open water cooled tower: Air contacts water directly
Closed loop cooling tower: Air cools a heat exchanger coil, isolating process water
Mechanical draft towers: Fans control air flow
Natural draft towers: Air flow driven by buoyancy
Regardless of type, airflow must be sufficient to meet the system’s thermal load.
If air flow is too low:
Water outlet temperature rises
Cooling capacity drops
Equipment may overheat
If air flow is too high:
Fan power consumption increases
Operating costs rise
Excessive evaporation increases cooling tower water use
Correct air flow ensures a balance between performance and energy efficiency.
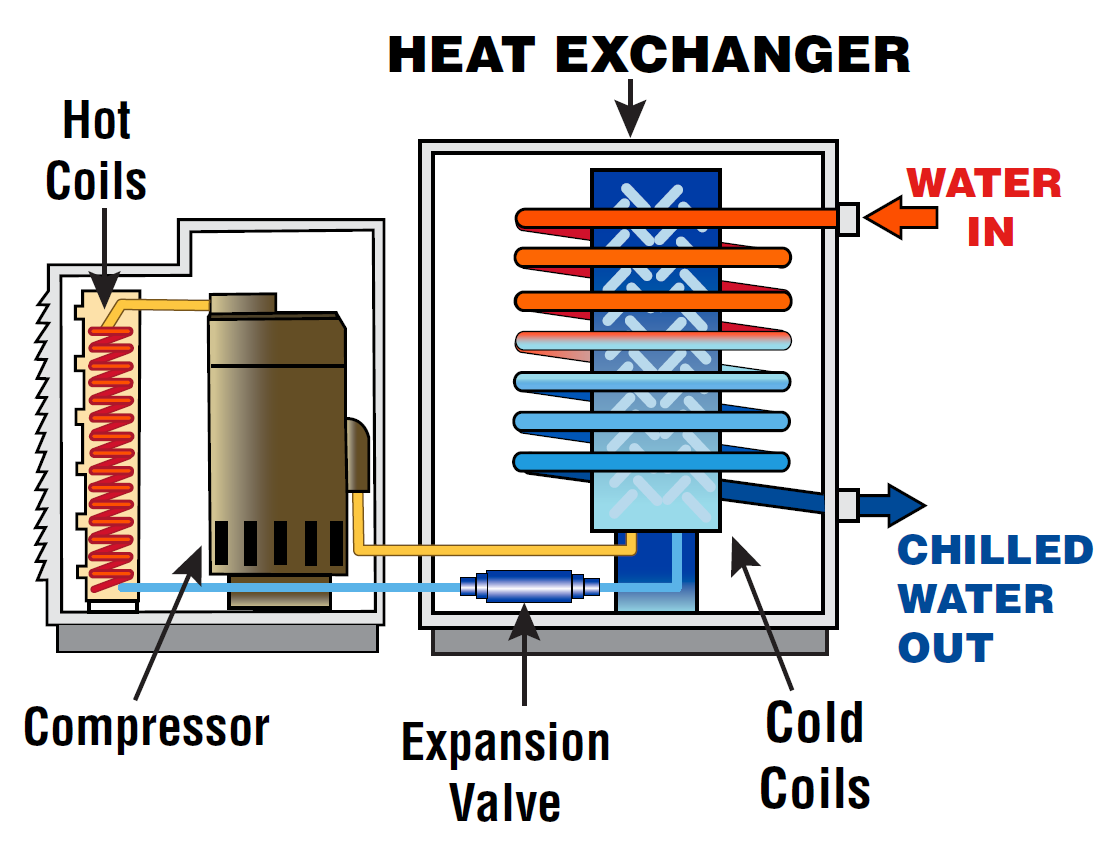
Air flow also affects:
Cooling tower water supply requirements
Evaporation losses
Drift and blowdown rates
Therefore, airflow calculations must align with cooling tower water testing and a reliable cooling tower water treatment system.
The total heat to be rejected is the foundation of airflow calculation:

Where:

The ambient wet bulb temperature sets the theoretical cooling limit. Lower wet bulb temperatures allow:
Less required air flow
Lower fan energy consumption
Wet bulb temperature is a critical design input for every water cooling tower.
Air density and specific heat vary with temperature and altitude. Typical design values:
Air density: 1.15–1.25 kg/m³
Specific heat of air: ~1.005 kJ/kg·°C
The most commonly used approach is based on heat transfer to air:

Cooling tower fans are rated in volumetric flow (m³/s):

This value is used for fan selection and tower sizing.
Engineers often use the L/G ratio:

Typical L/G ratios depend on:
Tower fill type
Design approach temperature
Whether the system is open or closed loop cooling tower
Manufacturers such as Mach Cooling provide optimized L/G ranges for each tower model.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Water flow rate | 900 m³/h |
| Water inlet temperature | 40 °C |
| Water outlet temperature | 30 °C |
| Heat load | 10,500 kW |
| Air temperature rise | 8 °C |
| Air density | 1.2 kg/m³ |


This airflow value guides fan selection and tower geometry design.
Higher air flow increases evaporation. Adequate water supply capacity is required to maintain stable operation without interruptions.
Changes in airflow influence concentration cycles. Regular testing of:
Conductivity
pH
Hardness
ensures consistent heat transfer and protects internal components.
An effective treatment program reduces fouling and scaling, allowing the designed air flow rate to deliver full cooling performance without unnecessary fan power increases.
By accurately calculating air flow rate:
Fan energy is minimized
Evaporation losses are controlled
Overall cooling tower water use is optimized
This is especially important in regions with water scarcity.
| Cooling Tower Type | Typical Air Flow Range |
|---|---|
| Water cooled tower | Medium to high |
| Closed loop cooling tower | Medium |
| High-efficiency industrial tower | Optimized by L/G ratio |
Understanding how to calculate air flow rate in a cooling tower is fundamental for designing and operating an efficient water cooling tower system. By combining heat balance principles, air property data, and practical L/G ratios, engineers can accurately determine the required airflow for any water cooled tower or closed loop cooling tower.
Accurate airflow calculation supports:
Stable cooling performance
Reduced energy consumption
Controlled cooling tower water use
Reliable water chemistry management through proper cooling tower water testing and treatment
Professional manufacturers such as Mach Cooling (https://www.machcooling.com/) integrate these principles into their cooling tower designs, helping users achieve long-term reliability and efficiency.
Top 5 Cooling Tower Manufacturers in Afghanistan by Performance And Sustainability in 2026
2026 TOP 8 Leading Cooling Tower Companies in Bhutan: Who’s Pioneering Innovation
Top 5 Rated Cooling Tower Manufacturers in Maldives for Commercial And Industrial Use
2026 Top 10 Ranking The Best Cooling Tower Companies in Nepal: Who Makes The Most Efficient Systems
Best Cooling Tower Manufacturers in Bangladesh: TOP 5 Ranking And Industry Insights
Cooling Tower Manufacturer Rankings in Pakistan: Who’s at The Top?
Top 10 Cooling Tower Manufacturers in India You Need To Know in 2026
Leading Cooling Tower Companies in Mongolia: The Best Brands for Efficiency And Reliability
Cooling Tower Manufacturers Ranking in South Korea: Who’s Leading The Market in 2026
The Top 5 Cooling Tower Companies in Japan Revolutionizing Heat Management in 2026